UniCAP
A Unified Computing Engine For Fast Data Processing
UniCAP: A Unified Computing Engine for Fast Data Processing
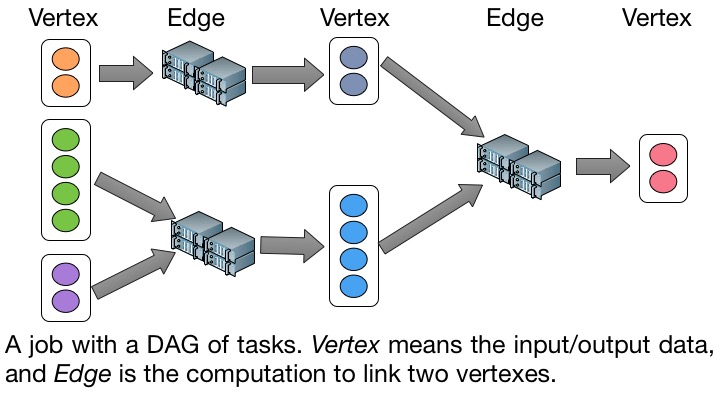
The UniCAP project is a distributed computing engine for executing data parallel programmes, which consist of a complex of directed-acyclic-graph (DAG) of tasks. It unifies Batch Processing and Stream Processing in one system using a timed dataflow model. Clients can either use UniCAP in NTU Big Data Platform (BDP), or build from source codes.
The main design features of UniCAP are:
Timed Dataflow
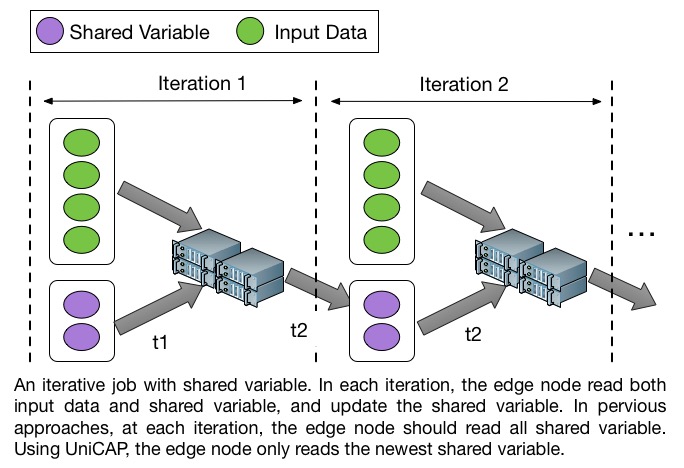
Timed Dataflow aims at reducing the communication overhead for iterative jobs with shared variables. In such jobs, the edge node reads input data and shared variables, and updates the shared variables at each iteration. This kind of application includes:
- Supervised Machine Learning: To train a model, the supervised machine learning applications (e.g., logistic regression, artificial neural network, etc.) need to update the parameters, which are the shared variables, based on the input data and old parameters at each iteration.
- Graph Processing: The graph processing jobs (e.g., single source shortest path, pagerank, etc.) usually update the graph nodes’ weights, which are the shared variables, based on the graph data and old weights at each iteration.
Precious approaches like Hadoop, Spark have high communication overhead to fetch all the shared variables at each iteration. Our experiments show that the shared variable query time can take up to 60% of total execution time of an iteration. However, our experiments also show that a large part of shared variables are static values during the computation. However, previous approaches always fetch all the shared variables, even if there is no change.
Time Dataflow tackles this problem by adding logical timestamp to the shared variables. Thus, at each iteration, the computation nodes (which caches the old shared variables in previous iteration) only need to fetch the changed shared variables rather than all the shared variables. Experiments show that timed dataflow can accelerate logistic regression and pagerank 30% and 45% respectively, compared to Spark.
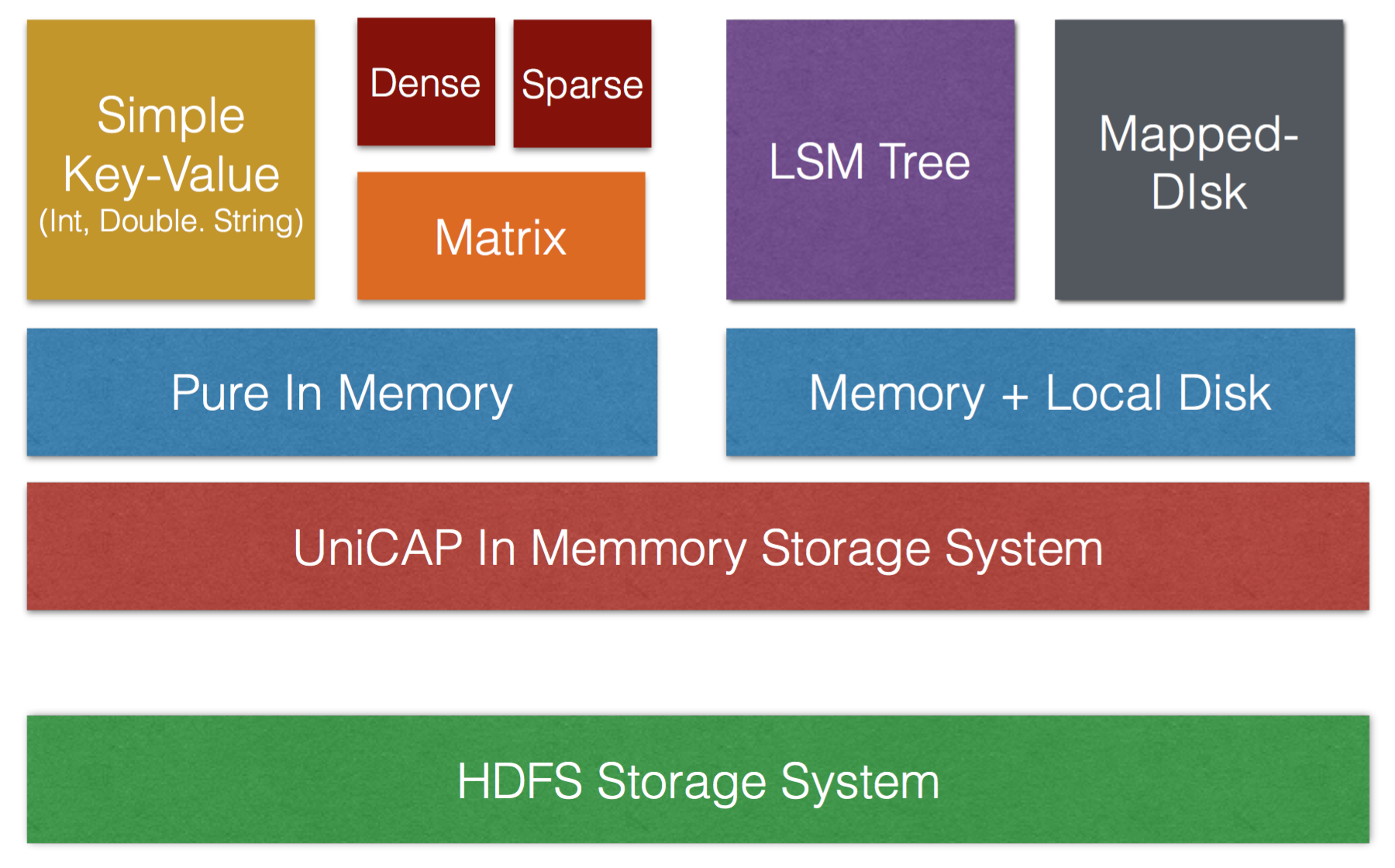
Hybrid Vertex
UniCAP embodies a set of storage systems as its Vertexes. Generally, UniCAP can support both pure-memory and mix memory-disk storage.
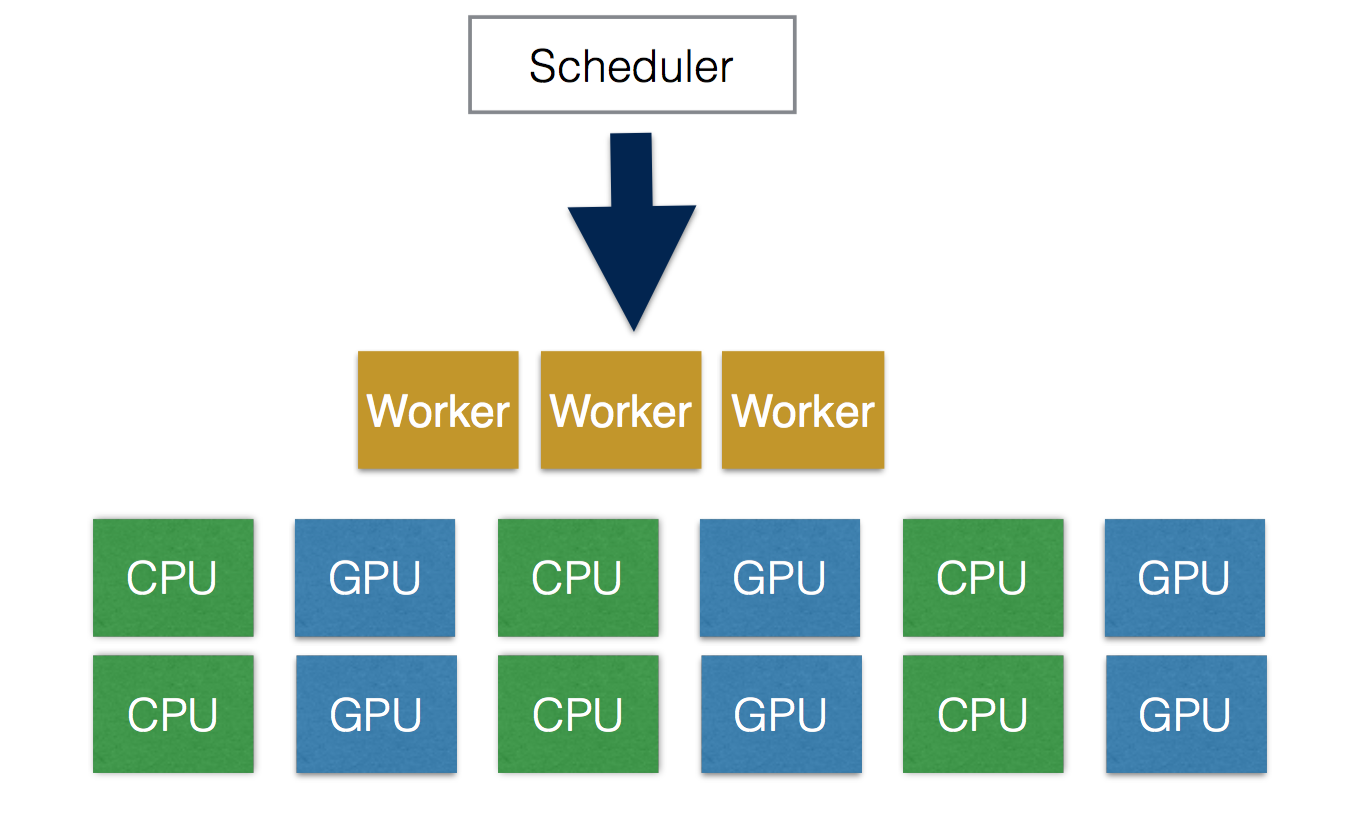
Hybrid Edge (In Development)
UniCAP supports schedule tasks using both GPU and CPU in a single application. Compared to other approaches, which can only use CPU or GPU, UniCAP maximize the system resource utilization.